Levels Of Organization Answer Key
Learning Outcomes
- Lodge the levels of organization of living things
Living things are highly organized and structured, post-obit a hierarchy that tin be examined on a scale from small to large. The atom is the smallest and most fundamental unit of matter. It consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atoms form molecules. A molecule is a chemical structure consisting of at to the lowest degree two atoms held together by 1 or more chemic bonds. Many molecules that are biologically important are macromolecules, big molecules that are typically formed by polymerization (a polymer is a large molecule that is made by combining smaller units chosen monomers, which are simpler than macromolecules). An example of a macromolecule is deoxyribonucleic acid (Dna) (Figure 1), which contains the instructions for the structure and operation of all living organisms.

Figure ane. All molecules, including this Dna molecule, are composed of atoms. (credit: "brian0918″/Wikimedia Eatables)
Some cells contain aggregates of macromolecules surrounded by membranes; these are chosenorganelles. Organelles are small structures that exist within cells. Examples of organelles include mitochondria and chloroplasts, which behave out indispensable functions: mitochondria produce energy to power the jail cell, while chloroplasts enable green plants to utilize the free energy in sunlight to make sugars. All living things are fabricated of cells; the prison cell itself is the smallest fundamental unit of structure and function in living organisms. (This requirement is why viruses are not considered living: they are not made of cells. To make new viruses, they have to invade and hijack the reproductive machinery of a living cell; only then can they obtain the materials they need to reproduce.) Some organisms consist of a unmarried jail cell and others are multicellular. Cells are classified as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are single-celled or colonial organisms that practise non have membrane-bound nuclei or organelles; in contrast, the cells of eukaryotes do take membrane-spring organelles and a membrane-jump nucleus.
In larger organisms, cells combine to maketissues, which are groups of similar cells carrying out similar or related functions. Organs are collections of tissues grouped together performing a common office. Organs are present not simply in animals but also in plants. An organ organization is a higher level of organisation that consists of functionally related organs. Mammals have many organ systems. For instance, the circulatory system transports blood through the body and to and from the lungs; it includes organs such as the eye and blood vessels. Organisms are individual living entities. For example, each tree in a wood is an organism. Single-celled prokaryotes and single-celled eukaryotes are also considered organisms and are typically referred to as microorganisms.
All the individuals of a species living within a specific area are collectively chosen apopulation. For example, a wood may include many pino trees. All of these pino copse represent the population of pine trees in this forest. Different populations may live in the same specific expanse. For example, the woods with the pine trees includes populations of flowering plants and also insects and microbial populations. A community is the sum of populations inhabiting a particular area. For instance, all of the trees, flowers, insects, and other populations in a forest form the woods's community. Keep in mind that the community level only consists of living organisms. The forest itself is an ecosystem; this is the first level that contains non-living aspects of a given surface area that impact the living things in that environment. An ecosystem consists of all the living things in a particular area together with the abiotic, non-living parts of that environment such as nitrogen in the soil or pelting h2o. At the highest level of arrangement (Figure ii), the biosphere is the collection of all ecosystems, and it represents the zones of life on earth. It includes land, h2o, and fifty-fifty the atmosphere to a sure extent.
Practice Question
From a unmarried organelle to the entire biosphere, living organisms are parts of a highly structured hierarchy.
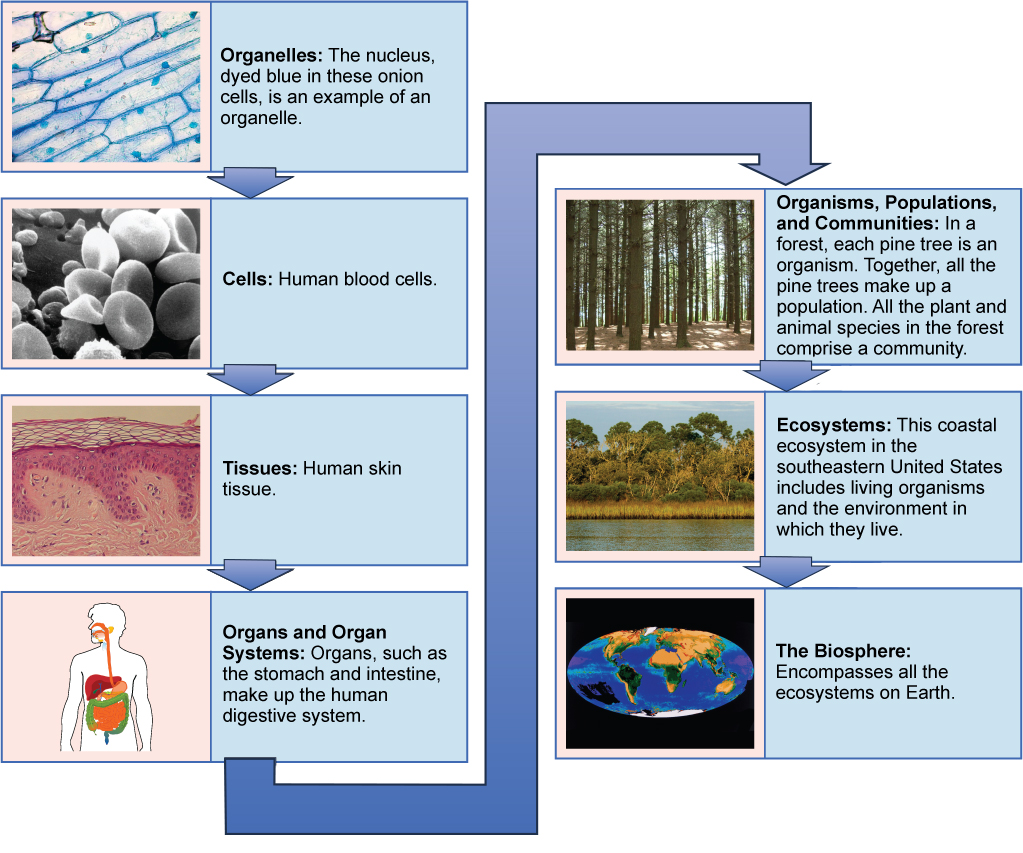
Effigy 2. The biological levels of organization of living things are shown. From a single organelle to the entire biosphere, living organisms are parts of a highly structured hierarchy. (credit "organelles": modification of work by Umberto Salvagnin; credit "cells": modification of work by Bruce Wetzel, Harry Schaefer/ National Cancer Institute; credit "tissues": modification of work past Kilbad; Fama Clamosa; Mikael Häggström; credit "organs": modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal; credit "organisms": modification of work by "Crystal"/Flickr; credit "ecosystems": modification of work by US Fish and Wild animals Service Headquarters; credit "biosphere": modification of work by NASA)
Which of the post-obit statements is imitation?
- Tissues be within organs, which exist inside organ systems.
- Communities exist within populations, which exist inside ecosystems.
- Organelles exist within cells, which exist within tissues.
- Communities exist within ecosystems, which exist in the biosphere.
Show Answer
Statement b is false: populations exist within communities.
Try It
Contribute!
Did you lot have an idea for improving this content? We'd love your input.
Improve this pageLearn More
Levels Of Organization Answer Key,
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-biology2/chapter/levels-of-organization-of-living-things/
Posted by: cookesweaver.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Levels Of Organization Answer Key"
Post a Comment